Key Considerations When Implementing ERP in Healthcare Organizations
1. Compliance with Regulatory Standards
One of the most critical factors in the healthcare industry
is ensuring that all operations comply with regulatory standards such as the
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. or the
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. These regulations are
designed to protect patient information and ensure data privacy. An ERP system
must be capable of securely managing sensitive data, including electronic
health records (EHR) and patient billing information, while meeting stringent
compliance requirements.
Before selecting an ERP solution, healthcare organizations
should ensure that it includes robust security features such as data
encryption, role-based access controls, and audit trails. Additionally, regular
updates and compliance reviews are essential to keep up with evolving
regulatory requirements.
2. Integration with Existing Systems
Healthcare organizations typically use a wide array of
specialized software solutions, from electronic medical records (EMR) systems
to patient management, lab information, and billing systems. A key challenge in
ERP implementation is ensuring seamless integration with these legacy systems.
Without proper integration, data silos can develop, leading to inefficiencies
and inaccuracies in information sharing.
The selected ERP system must offer integration capabilities
that allow it to work with other essential healthcare systems. Interoperability
is crucial for maintaining continuity of care and enabling data sharing across
departments. A healthcare ERP solution should also support standardized
communication protocols such as HL7 (Health Level 7) and FHIR (Fast Healthcare
Interoperability Resources) to ensure compatibility with other medical systems.
3. Focus on Patient-Centric Care
Unlike other industries, healthcare's primary focus is on
delivering quality patient care. When implementing an ERP system, it is crucial
to consider how it will enhance the patient experience. For instance, an ERP
system can streamline patient scheduling, reduce waiting times, and improve
access to medical records, leading to better patient outcomes.
Healthcare ERP systems should include modules that
specifically support clinical operations, such as managing patient records,
tracking treatment plans, and monitoring patient outcomes. A well-implemented
ERP system can help improve care coordination, reduce the risk of medical
errors, and enable healthcare providers to spend more time focusing on patient
care rather than administrative tasks.
4. Customization and Scalability
Healthcare organizations vary significantly in size and
scope, from small clinics to large hospital networks. As such, the ERP system
should be customizable to meet the specific needs of the organization. It
should allow for flexibility in configuring workflows, reporting, and other
processes according to the unique requirements of the healthcare provider.
In addition to customization, scalability is an important
consideration. Healthcare organizations often expand, whether by opening new
facilities, integrating with other providers, or adding new service lines. An
ERP system must be able to scale with the organization’s growth without
compromising performance or user experience.
5. Change Management and Training
ERP implementations often face resistance from staff,
especially in the healthcare industry where employees are accustomed to
established workflows and systems. A successful ERP implementation depends not
only on the technology but also on how well staff members are trained and how
smoothly the transition to the new system is managed.
Change management strategies should be in place to guide
staff through the transition. This includes clear communication about the
benefits of the new system, comprehensive training programs to ensure staff
members can use the system efficiently, and ongoing support
post-implementation. Involving clinical and administrative staff in the
selection and design process can also help minimize resistance and ensure that
the system meets the needs of all users.
6. Data Analytics and Reporting
One of the major benefits of an ERP system is the ability to
gather and analyze data across the organization. For healthcare providers, data
analytics can provide insights into patient outcomes, resource utilization,
financial performance, and operational efficiency. The ERP system should offer
advanced reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling healthcare
organizations to make data-driven decisions that enhance patient care and
streamline operations.
Real-time reporting can also assist in compliance
monitoring, helping organizations stay aligned with regulatory requirements.
Additionally, predictive analytics can be used to forecast patient demand,
optimize staffing levels, and improve inventory management, ultimately leading
to better service delivery.
7. Cost Considerations and ROI
While ERP systems can offer significant long-term benefits,
the upfront costs of implementation can be substantial. Healthcare
organizations should evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) of an ERP system,
including licensing, customization, training, and ongoing maintenance. A
cost-benefit analysis should be conducted to determine the expected return on
investment (ROI).
The potential savings from streamlined processes, reduced
administrative overhead, and improved patient care should be weighed against
the initial investment. In many cases, the right ERP system can lead to
improved operational efficiencies, lower costs, and enhanced patient
satisfaction, making the investment worthwhile.
Conclusion
Implementing an ERP system in healthcare organizations is a
complex but rewarding process. By carefully considering factors such as
compliance, integration, patient care, scalability, and staff training,
healthcare providers can leverage ERP to streamline operations and enhance
patient outcomes. A well-executed ERP implementation can not only improve
internal efficiency but also position healthcare organizations to deliver
higher-quality care in a rapidly evolving industry.
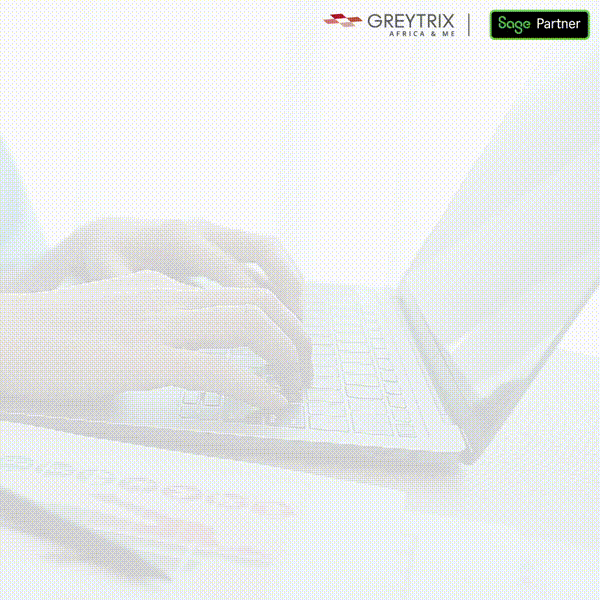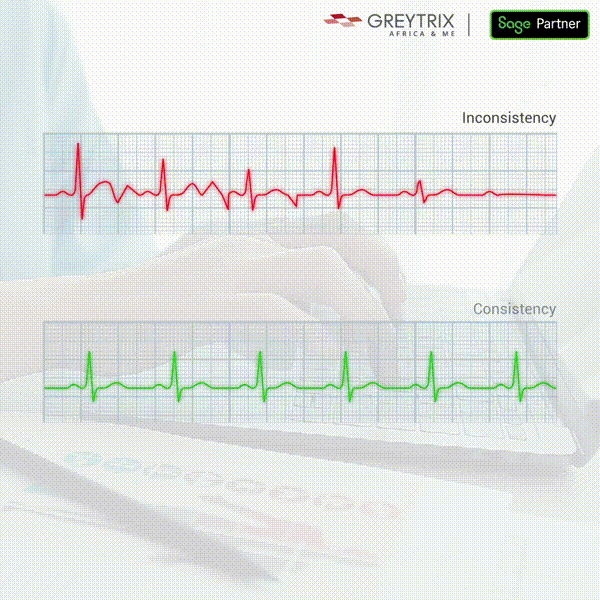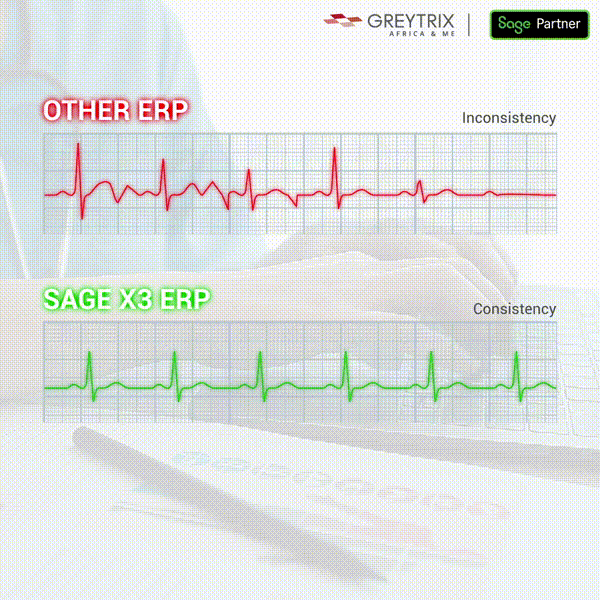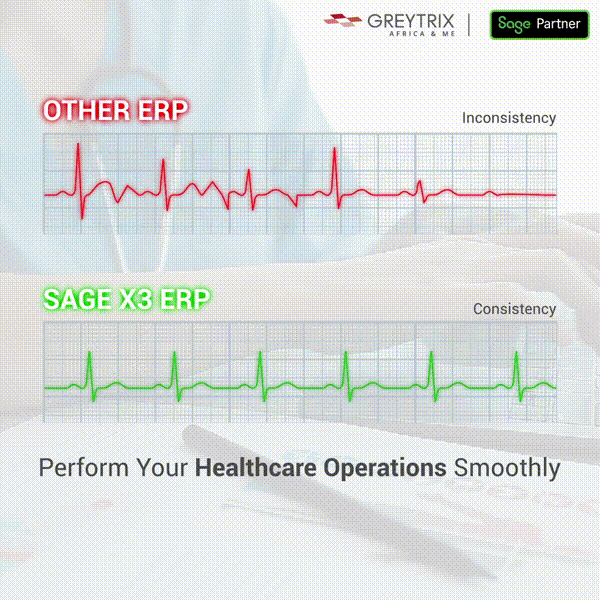



Comments
Post a Comment